News

#SIRIUSDiscoveries
A new study on the willow cultivar Salix miyabeana ‘SX64’ reveals a highly sophisticated aspect of plant salt tolerance. The study demonstrates that the willow's metabolic response to soil salinity is vastly different depending on the specific salt anion present.
This detailed investigation was done using untargeted metabolomics, detecting over 5,000 metabolic compounds across the willow's roots, stems, and leaves. Interpreting this vast and complex dataset required advanced computational tools. The researchers used SIRIUS to identify the chemical structures of unknown compounds from mass spectrometry data.
This detailed investigation was done using untargeted metabolomics, detecting over 5,000 metabolic compounds across the willow's roots, stems, and leaves. Interpreting this vast and complex dataset required advanced computational tools. The researchers used SIRIUS to identify the chemical structures of unknown compounds from mass spectrometry data.
#SIRIUSFeature
Molecular Structure Annotation:
SIRIUS uses the predicted molecular fingerprint to efficiently search massive molecular structure databases (like PubChem) and identify the most likely structure candidate for your unknown compound.
SIRIUS uses the predicted molecular fingerprint to efficiently search massive molecular structure databases (like PubChem) and identify the most likely structure candidate for your unknown compound.

Uncovering a Key to Coral Heat Tolerance
New research offers key insights into how coral symbionts adapt to heat stress at a molecular level.
This in-depth biochemical analysis was conducted using untargeted metabolomics and chemical classification of metabolite features was performed using SIRIUS.

The secrets of healing mushrooms
A recent study details the genetic and metabolic basis for the production of sesquiterpenoids in the medicinal mushroom Sanghuangporus, which is highly valued in East Asian medicine for its therapeutic properties.
SIRIUS was instrumental in effectively identifying the target cluster of sesquiterpenoids from the mushroom extracts when combined with feature-based molecular networking. It provided molecular formula and substructure annotations for the compounds within the target cluster based on their fragmentation patterns.
SIRIUS was instrumental in effectively identifying the target cluster of sesquiterpenoids from the mushroom extracts when combined with feature-based molecular networking. It provided molecular formula and substructure annotations for the compounds within the target cluster based on their fragmentation patterns.
#SIRIUSFeature
Molecular Fingerprint Prediction
SIRIUS predicts a compound's unique, machine-readable molecular fingerprint (a set of structural properties) from the fragmentation pattern. This crucial, intermediary feature powers highly accurate structure and class prediction.
SIRIUS predicts a compound's unique, machine-readable molecular fingerprint (a set of structural properties) from the fragmentation pattern. This crucial, intermediary feature powers highly accurate structure and class prediction.
Hidden Players in Drug Efficacy
In pharmacology, one of the most significant challenges is the variability in how patients respond to the same drug. While factors like genetics and lifestyle are known to play a role, emerging research points to a hidden player: the human gut microbiota.
Using SIRIUS, a recent study identified novel metabolic pathways where bacteria can either activate or inactivate medications.
Using SIRIUS, a recent study identified novel metabolic pathways where bacteria can either activate or inactivate medications.
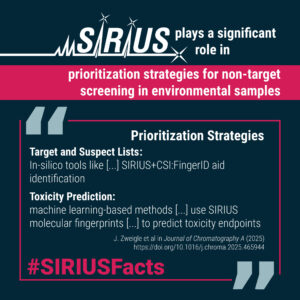
Prioritization strategies
SIRIUS plays a significant role in prioritization strategies for non-target screening in environmental samples. Its primary function is to generate molecular fingerprints from MS/MS data, which are then used for compound identification or toxicity prediction.
#SIRIUSFeature
Network-Enhanced Molecular Formula Annotation:
For complex biological datasets, SIRIUS improves the accuracy of molecular formula annotations by analyzing relationships across the entire dataset. It re-ranks the initial molecular formula candidates using a sophisticated network-based algorithm that leverages the fact that related compounds often share similarities in their biosynthetic pathways and fragmentation patterns.
For complex biological datasets, SIRIUS improves the accuracy of molecular formula annotations by analyzing relationships across the entire dataset. It re-ranks the initial molecular formula candidates using a sophisticated network-based algorithm that leverages the fact that related compounds often share similarities in their biosynthetic pathways and fragmentation patterns.
#SIRIUSDiscoveries
New research reveals the significant role of plant root lipids in soil carbon dynamics, offering new avenues for enhancing long-term carbon storage.
SIRIUS compound class prediction was essential for annotating 80% of the previously unknown metabolite features, with 'Organic acids and derivatives' and 'Lipid and lipid-like molecules' being the most predominant chemical superclasses.
SIRIUS compound class prediction was essential for annotating 80% of the previously unknown metabolite features, with 'Organic acids and derivatives' and 'Lipid and lipid-like molecules' being the most predominant chemical superclasses.

Meet us at ASMS 2026
We have secured our spot for ASMS2026 in sunny San Diego! ☀️
If you're attending, make sure to visit us at our booth next to the main entrance.
We truly look forward to meeting many of you to discuss how SIRIUS will improve your small molecule analysis.
If you're attending, make sure to visit us at our booth next to the main entrance.
We truly look forward to meeting many of you to discuss how SIRIUS will improve your small molecule analysis.
#SIRIUSFacts
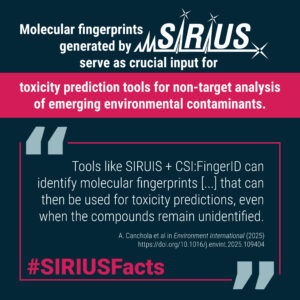
Although direct structural information may not always be available, specific structural details, such as the presence of function groups, can be obtained from MS/MS spectra using SIRIUS. These molecular fingerprints serve as crucial inputs for other predictive models, such as toxicity predictions, even when the exact identity of a compound is unknown.

#SIRIUSFeature
Molecular Formula Annotation:
SIRIUS delivers accurate molecular formula annotation by employing a powerful dual approach that analyzes both high-resolution isotope patterns and complex fragmentation patterns. This process proposes and scores the most accurate elemental composition without needing a spectral library.
SIRIUS delivers accurate molecular formula annotation by employing a powerful dual approach that analyzes both high-resolution isotope patterns and complex fragmentation patterns. This process proposes and scores the most accurate elemental composition without needing a spectral library.
#SIRIUSDicoveries
A new study from the long-running The Jena Experiment challenges a core ecological assumption: that in a diverse ecosystem, plants can save energy on defenses and focus on growth.
Using untargeted metabolomics and SIRIUS for feature annotation researchers found that plant life in a biodiverse community is not a break from pests but an intense battle for resources. Competition for light and nutrients forces plants into a complex balancing act, with leaves becoming physically weaker and roots tougher. In parallel, plants increase their chemical arsenal to compensate for physical defenses.

#SIRIUSDiscoveries
Is breast cancer risk linked to drinking water quality? Potential link between chemicals in drinking water and regional differences in breast cancer incidence in California.
#SIRIUSFeature
Integrated LC/MS Preprocessing:
Stop wrestling with complex LC/MS data cleanup!
SIRIUS offers integrated preprocessing tools that automate the essential, time-consuming steps of preparing your complex LC/MS data for high-throughput analysis.
Stop wrestling with complex LC/MS data cleanup!
SIRIUS offers integrated preprocessing tools that automate the essential, time-consuming steps of preparing your complex LC/MS data for high-throughput analysis.

Making small molecule annotation more accessible
mzio and Bright Giant have partnered to seamlessly connect mzmine with SIRIUS. Today we are thrilled to present this one-click, automated integration to deliver a rapid and convenient non-targeted analysis experience.
SIRIUS in space
A recent study by researchers at UC San Diego has provided the most extensive look yet at the microbial and chemical landscape of the ISS. Using multi-omic sequencing and untargeted metabolomics, they created a comprehensive 3D map of the space station's surfaces.
Only about 3% of the chemical features could be annotated by matching them against existing spectral libraries. This "dark matter" of unknown molecules required advanced computational tools. Our SIRIUS software was used to tackle this unknown territory, dramatically increasing the characterization of these molecules from 3% to nearly 97%! This allowed researchers to identify distinct "chemical hotspots" linked to different module functions, from corrosion inhibitors near exercise equipment to urinary metabolites near the hygiene unit.
Only about 3% of the chemical features could be annotated by matching them against existing spectral libraries. This "dark matter" of unknown molecules required advanced computational tools. Our SIRIUS software was used to tackle this unknown territory, dramatically increasing the characterization of these molecules from 3% to nearly 97%! This allowed researchers to identify distinct "chemical hotspots" linked to different module functions, from corrosion inhibitors near exercise equipment to urinary metabolites near the hygiene unit.

SIRIUS In the Pipeline
We are absolutely honored and excited that our newest publication on our tag-free screening platform has been highlighted by Derek Lowe on his Science Magazine blog, "In the Pipeline", about drug discovery and the pharma industry.

#SIRIUSDiscoveries
Ethanol vs methanol: Safe off-site collection of human fecal samples.
This study using SIRIUS and CANOPUS demonstrates that a 95% ethanol extraction of the Matrix Method represents a valid, safer, and more economical alternative for large-scale gut microbiome research.
This study using SIRIUS and CANOPUS demonstrates that a 95% ethanol extraction of the Matrix Method represents a valid, safer, and more economical alternative for large-scale gut microbiome research.
Tag-free Screening
Our recent study introduces a major leap forward in affinity selection screening for early drug discovery: Self-Encoded Libraries. Our approach uses advanced mass spectrometry to screen hundreds of thousands of small molecules in a single experiment, bypassing the significant limitations of traditional high-throughput screening as well as affinity selection with barcoded libraries. It allows drug discovery teams to identify high-affinity drug candidates faster, more affordably, and against targets previously inaccessible to common screening methods.
